How do solar panels work? Little by little, solar panels have become an integral part of the urban landscape. If you look at the roofs of newly constructed buildings, you will likely find them, as they are mandatory in most cases.
They can also be seen atop the less favoured “parking meters” or the even more unpopular speed cameras.

But how do solar panels work?
This is how the energy of the sun is harnessed. To sum up, the process is as follows:
The sun’s rays collide with plates composed of semiconductor materials, transforming the received energy into electricity. Solar panels convert light into electricity through a process known as the Photovoltaic Effect, collecting energy in the form of sunlight and capturing it as continuous energy.
On a more technical note, solar panels are comprised of several individual solar cells. They consist of layers of silicon, phosphorus, and boron. This specific composition allows the panels to absorb photons from sunlight, generating a direct electrical current. This current is then transformed into a usable alternating current, made possible by an inverter. All this is known as the Photovoltaic Effect – a physical phenomenon involving the emission of photoelectrons by a material when it receives light energy. This phenomenon enables us to harness solar energy for electricity production.
How solar cells work
Solar cells, combined with other components like phosphorus and boron, form two parts: one charged with negative electrons and the other with positive ones.
When exposed to sunlight, photons move electrons from the part with excess negative charge to the part where it is lacking. This movement creates Solar Self-Consumption energy.
As photons release electrons, more and more electricity is generated. Unused electrons or those from the wind return to the negative panel, initiating the process anew in an endless cycle.
This produces direct current, stored in batteries until it is converted into alternating current (which powers your home) through voltage inverters.
What are voltage inverters?
It’s essential to know that direct current, as the name indicates, flows in one direction to understand the function of these devices.
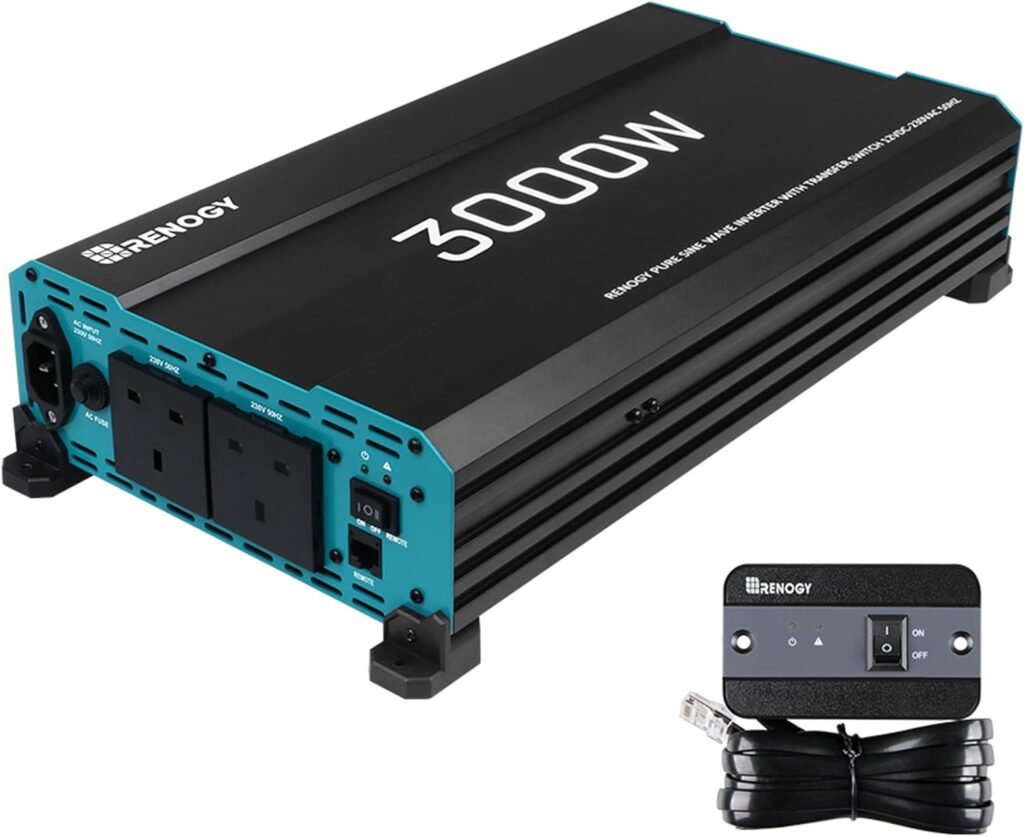

In contrast, alternating current constantly changes power and direction with various intervals of valleys and peaks.
Voltage inverters smoothly and constantly change the direction of direct current, converting it into alternating current. Why? To be usable to you, most appliances require alternating current to function. Also, home appliances like refrigerators, dishwashers, and mini-chains require a specific and well-regulated voltage. So, this is easier to achieve with alternating current.
Do solar panels work when it rains?
We find the answer to this question so easy – yes, solar panels indeed operate during rainy weather. Even if it’s raining or there’s a thunderstorm, your system continues to generate energy. Admittedly, it may not match the output of a radiant, sunny day, but the modules consistently produce energy.
During rain and cloudiness, solar panels generate between 30% and 50% of their production on cloudy days and between 10% and 20% on days of heavy rain.
Besides, rainy days clean the layers of dust, sand, or dirt accumulated on the top of the solar panels. Besides, rainy days clean the layers of dust, sand, or dirt accumulated on the top of the solar panels. Then, solar panels keep producing energy suitable for self-consumption. And thanks to the rain, the entire installation is cleaned without cleaning at specific intervals



Leave a Reply