What is a solar carport? They have emerged as a functional way to harness the power of the sun. So, let’s dig into the world of solar carports, exploring their functionality, pros, cons, and how they compare to traditional options.
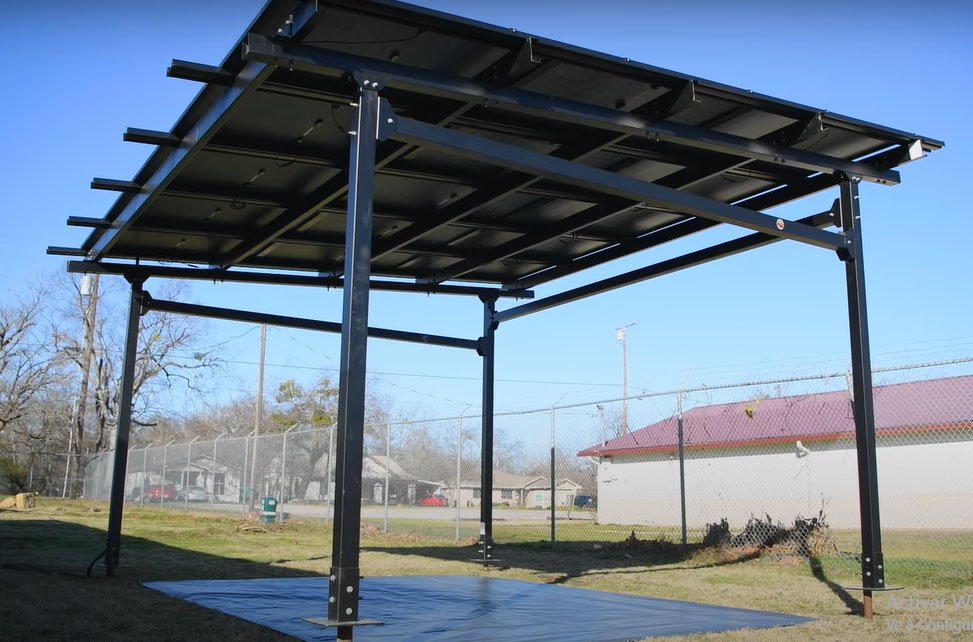

What Is A Solar Carport?
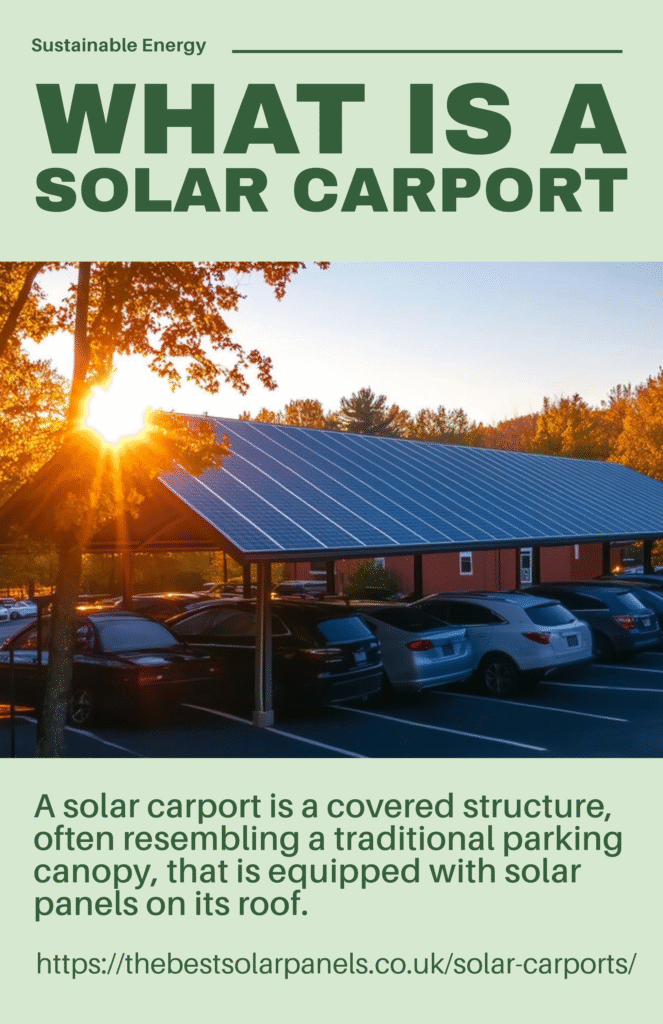
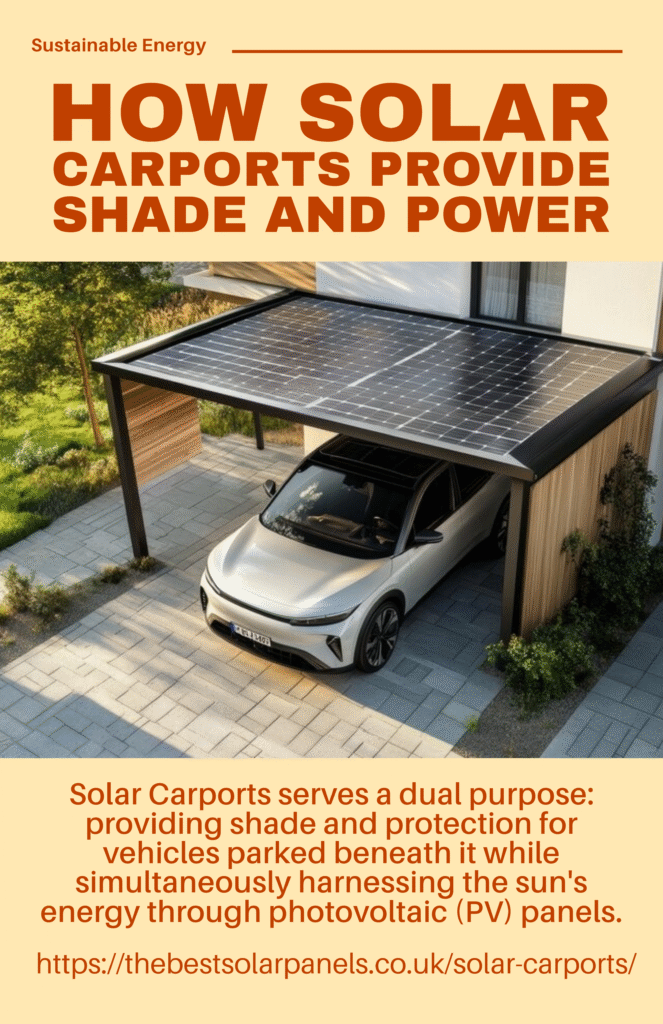
To start with, a solar carport is a covered structure, often resembling a traditional parking canopy, that is equipped with solar panels on its roof. As a result, this innovative structure serves a dual purpose: providing shade and protection for vehicles parked beneath it while simultaneously harnessing the sun’s energy through photovoltaic (PV) panels.
Key Features of a Solar Carport:
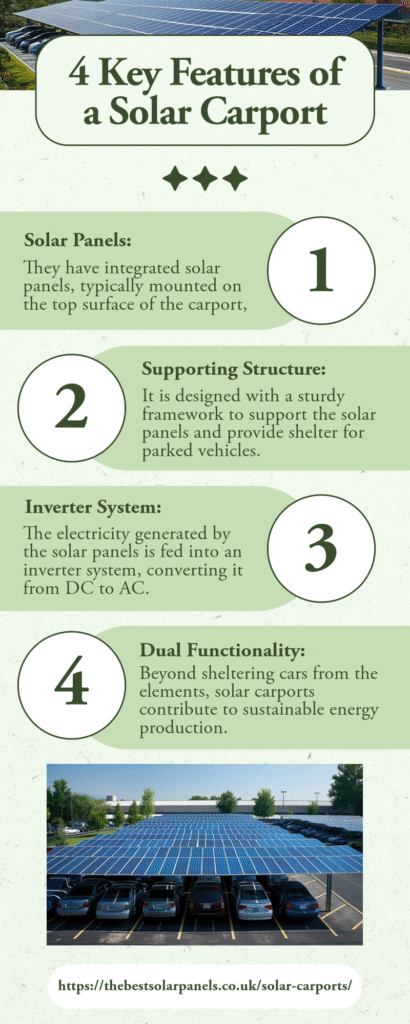
- Solar Panels: First, they have Integrated solar panels, typically mounted on the top surface of the carport, capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Supporting Structure: Also, the carport is designed with a sturdy framework to support the solar panels and provide shelter for parked vehicles.
- Inverter System: The electricity generated by the solar panels is fed into an inverter system, converting it from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for use or distribution.
- Dual Functionality: Beyond sheltering cars from the elements, solar carports contribute to sustainable energy production, reducing reliance on conventional power sources.
How Solar Carports Work
Solar carports work by incorporating photovoltaic (PV) solar panels into the structure’s design. But how do they work? Keep reading if you want to know more details.
1. Absorbing Sunlight with Photovoltaic Panels:
At the heart of every solar carport are photovoltaic (PV) panels, typically mounted on the top surface of the structure. So, these panels are made up of numerous photovoltaic cells, each capable of converting sunlight into electricity.
2. Electron Excitation and Electricity Generation:
When exposed to sunlight, the PV cells undergo a process known as the photovoltaic effect. So, sunlight consists of photons, which, upon striking the surface of the solar panels, excite electrons in the cells. Lastly, this excitation creates an electron flow, generating direct current (DC) electricity within the solar cells.
3. Directing Electricity to Inverter Systems:
The generated DC electricity is then channelled to an inverter system. In other words, the inverter plays a crucial role in converting the direct current into alternating current (AC), the form of electricity commonly used in homes, businesses, and the power grid.
4. Powering On-Site Facilities or Feeding Back to the Grid:
The AC electricity can be utilized in various ways:
On-Site Consumption: The electricity generated can be used to power nearby facilities, streetlights, or electric vehicle (EV) charging stations within the vicinity of the solar carport.
Grid Connection: Excess electricity not immediately consumed can be fed back into the power grid. As a result, this contributes to the overall energy supply and may even result in financial incentives through net metering programs.
5. Providing Shelter and Shade:
Simultaneously, the solar carport serves its traditional purpose – providing shelter for vehicles parked beneath it. So, this dual functionality enhances the efficiency and practicality of the structure, making it an innovative solution for sustainable energy production and parking infrastructure.
Pros and cons of solar carports
Pros
Cons
Advantages explained
- Clean Energy Generation: Solar carports harness solar power, a clean and renewable energy source, reducing dependence on non-renewable alternatives.
- Dual Functionality: Beyond providing shade for vehicles, solar carports contribute to energy production, making efficient use of space.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By using solar energy, these structures aid in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Vehicle Protection: Cars parked under solar carports benefit from protection against the elements, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
- Space Optimization: Efficient use of space by combining parking infrastructure with renewable energy generation, especially valuable in areas with limited space.
- Grid Independence: Solar carports offer a decentralized energy source, reducing reliance on centralized power grids.
- Potential for Incentives: In some regions, solar carport owners may be eligible for financial incentives or tax credits for contributing to renewable energy production.
Disadvantages explained
- Upfront Cost: Initial installation costs can be higher compared to traditional carports, making the upfront investment a potential barrier.
- Maintenance Requirements: Solar panels require periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, as dirt, debris, and weather conditions can affect efficiency.
- Site-Specific Challenges: The effectiveness of solar carports can be influenced by site characteristics, including location, sunlight exposure, and potential shading.
- Visual Impact: Some may find the appearance of solar carports less visually appealing than traditional structures, impacting aesthetic considerations.
- Land Use: Large-scale solar carports may require significant land use, potentially leading to concerns in densely populated areas.
- Weather Dependence: Solar carports depend on sunlight for energy production, making them susceptible to weather conditions and variations in sunlight availability.
- Technology Advancements: Rapid advancements in solar technology may lead to concerns about the potential obsolescence of existing systems.
Solar Carports vs Traditional Solar Installation
| Carport | Traditional | |
| Energy Generation | Solar carports generate clean, renewable energy while providing shaded parking spaces. However, they may have slightly lower energy production compared to optimized rooftop installations because of the structure’s design. | Rooftop solar installations can be optimized for maximum sun exposure, potentially leading to higher energy production. However, their use is limited to energy generation, without offering additional functionality like shading. |
| Space Utilization | Efficient use of space by combining parking infrastructure with energy generation, although the space underneath the carport may be limited for certain activities because of the supporting structure. | They utilize available roof space without occupying ground-level areas. |
| Aesthetics | They are modern and environmentally conscious, potentially enhancing the overall visual appeal. However, some people may find the structures less aesthetically pleasing than traditional rooftop solar installations. | Rooftop installations are less visible and seamlessly integrate into the existing structure, but some people may view solar panels as obtrusive. |
| Initial Investment | They typically involve a higher upfront cost because they combine the functionality of shading and energy generation. However, the potential for financial incentives or tax credits can offset initial costs. | They have generally lower upfront costs as they focus solely on energy generation, but they may lack some of the financial incentives associated with multifunctional structures like carports. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Regular maintenance is required for both the solar panels and the supporting carport structure | Maintenance is primarily focused on the solar panels themselves, so the supporting roof structure may require less maintenance than a full carport. |
| Shading Benefits | They provide shaded parking spaces, protecting vehicles from the elements and reducing interior temperatures. | They don’t provide shading benefits; focus solely on maximizing solar exposure for energy generation. |
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs, available space, budget, and aesthetic preferences.


Cost of solar carports
Determining the cost of solar carports can be influenced by various factors, including project size, location, design complexity, and the type of solar technology used. Here are key considerations when assessing the cost of solar carports:
1. Size and Capacity:
Project Scale: The size of the solar carport, measured in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW), directly impacts the overall cost. Also, larger installations typically require more materials and labour.
2. Design Complexity:
Architectural Design: Intricate or custom designs may incur higher costs because of engineering and construction complexities.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Incorporating solar carports into an existing structure or designing them to complement specific architectural features can influence costs.
3. Location:
Geographic Location: Solar exposure varies by region, affecting the energy production potential. On the other hand, in regions with ample sunlight, solar carports can be more cost-effective.
Local Regulations: Permitting and regulatory requirements can impact costs, with some areas offering incentives or rebates that offset expenses.
4. Structural Considerations:
Foundation Type: The type of foundation required for the carport structure—whether it’s surface-mounted, ballasted, or foundation-pier—can affect costs.
Wind and Snow Loads: Carports must be engineered to withstand local weather conditions, and additional structural support may be necessary in areas with high wind or snow loads.
5. Solar Technology:
Solar Panel Efficiency: High-efficiency solar panels may have a higher upfront cost but can maximize energy production over time.
Inverter Systems: The type and capacity of inverters that convert DC electricity to AC can impact costs.
6. Installation Costs:
Labour Costs: Installation costs, including labour, can vary based on local labour rates and the complexity of the installation.
Electrical Wiring and Connection: The cost of connecting the solar carport to the electrical grid and integrating it with on-site infrastructure.
7. Financial Incentives:
Government Incentives: The availability of federal, state, or local incentives, tax credits, or rebates can significantly reduce the overall cost.
Net Metering: Programs that allow excess energy generated to be fed back into the grid, potentially providing financial benefits.
8. Maintenance Costs:
Ongoing Maintenance: Regular maintenance costs, including cleaning solar panels and ensuring structural integrity, should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
9. Vendor and Installer:
Vendor Selection: The choice of solar panel manufacturer, carport structure supplier, and installer can impact costs.
Installer Experience: Experienced installers may command higher labour costs but can offer greater expertise and efficiency.
10. Financing Options:
Financing Terms: Finally, the financing terms, whether through loans, leases, or power purchase agreements (PPAs), can affect the overall financial structure of the project.

How to build a solar carport?
Building a solar carport involves careful planning, structural design, electrical considerations, and compliance with local regulations. Here is a general guide on how to build a solar carport:
1. Preliminary Planning:
- Determine Project Objectives: At first, define the purpose of the solar carport (e.g., energy generation, vehicle shading, or a combination of both).
- Site Assessment: Evaluate the location for solar exposure, considering factors like shading, orientation, and space availability.
- Budget and Financing: Finally, establish a budget and explore financing options, including potential government incentives or tax credits.
2. Design and Engineering:
- Architectural Design: Create a design that integrates seamlessly with the surroundings and meets aesthetic requirements.
- Structural Engineering: Engage a structural engineer to design a robust framework supporting solar panels and meeting local building codes.
- Foundation Design: Lastly, determine the appropriate foundation type (e.g., surface-mounted, ballasted, or foundation-pier) based on soil conditions and project requirements.
3. Obtain Necessary Permits:
- Local Regulations: Check local building codes and zoning regulations to ensure compliance. and obtain the necessary permits from local authorities.
4. Material and Component Selection:
- Solar Panels: Choose solar panels based on efficiency, output, and compatibility with the carport structure.
- Support Structure: Select materials for the supporting structure, considering durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
- Inverters and Electrical Components: Besides, you should determine the type and capacity of inverters needed for the system. Finally, plan the electrical wiring and connection to the grid.
5. Installation:
- Site Preparation: Clear the construction site and prepare the ground for the foundation.
- Structural Assembly: Construct the supporting framework according to the engineered design.
- Solar Panel Installation: Mount the solar panels securely on the structure, ensuring proper orientation and spacing.
- Electrical Wiring: Lastly, connect the solar panels to inverters and establish the electrical connections.
6. Grid Connection:
- Electrical Inspection: Schedule an inspection by local authorities to ensure compliance with electrical codes.
- Grid Connection: Connect the solar carport to the electrical grid, following local regulations and utility guidelines.
7. Ongoing Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of both the structural and electrical components.
- Cleaning: Also, clean solar panels regularly to ensure optimal energy production.
8. Monitoring and Optimization:
- Energy Monitoring: Implement a monitoring system to track energy production and system performance.
- Optimization: Besides, consider potential improvements or optimizations based on monitoring data.
9. Safety Considerations:
- Safety Measures: Implement safety measures during construction and ensure ongoing safety protocols.
- Emergency Procedures: Also, establish emergency procedures for maintenance and system operation.
10. Professional Assistance:
- Consult Professionals: Lastly, work with experienced solar installers, engineers, and electricians to ensure a successful and compliant installation. So, building a solar carport requires expertise in construction, electrical work, and solar technology.
How many solar panels do you need for a carport?
The number of solar panels needed for a carport depends on several factors, including energy requirements, available space, the efficiency of the solar panels, and the desired level of energy production. Here are the key steps to determine the number of solar panels for a carport:
1. Assess Energy Needs:
- Determine the energy consumption of the intended applications under the carport, such as lighting, electric vehicle charging stations, or other electrical devices.
2. Understand Solar Panel Capacity:
- Solar panels are typically rated in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). In other words, the capacity of a solar panel is a measure of its potential energy output under optimal conditions.
3. Calculate Daily Energy Production:
- Estimate the daily energy production required by converting the energy needs (step 1) to kilowatt-hours (kWh). So, this can be done by multiplying the power consumption (in kilowatts) by the number of hours the system is expected to operate.
4. Account for Solar Panel Efficiency:
- Also, consider the efficiency of the solar panels. Then, solar panel efficiency indicates how well a panel converts sunlight into electricity. So, higher-efficiency panels generate more power with the same amount of sunlight.
5. Consider Sunlight Conditions:
- Factor in the average sunlight conditions at the installation site because the amount of sunlight received affects the actual energy production.
6. Calculate Number of Panels:
- First, use the following formula to calculate the number of solar panels needed:
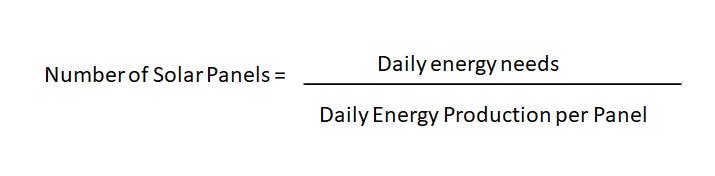
Ensure that all units are consistent (e.g., use kilowatt-hours for energy needs and panel capacity).
7. Include a Buffer:
- Add a buffer to the calculated number of panels to account for potential efficiency losses, shading, or variations in sunlight conditions.
8. Choose Panel Size:
- Then, select a standard solar panel size based on the calculated number. Common residential solar panels have capacities ranging from 250W to 400W or more.
9. Consult with Professionals:
- Finally, consult with solar professionals to get accurate estimates and ensure the system design aligns with local regulations and best practices.
Example Calculation:
- For example, if your daily energy needs are 20 kWh, and you choose 300W solar panels with an efficiency of 18%, the daily energy production per panel would be approximately 0.3×4.32≈1.30.3×4.32≈1.3 kWh (assuming 4.32 hours of sunlight). To meet the daily needs of 20 kWh, you would need approximately 20÷1.3≈1520÷1.3≈15 solar panels.
Keep in mind that these calculations are simplified, and real-world factors such as shading, orientation, and system losses should be considered for a more accurate estimate.
Can you charge your electric car with the solar carport?
Yes, you can charge your electric car using a solar carport. In fact, integrating electric vehicle (EV) charging stations with solar carports is a common and sustainable practice that aligns with the goals of reducing carbon emissions and promoting clean energy.
Conclusion
To sum up, solar carports represent a harmonious blend of sustainable technology and practical infrastructure. As we navigate towards a greener future, these shaded parking spaces not only protect our vehicles but also contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape.




Leave a Reply