What are perovskite solar cells? With their exceptional efficiency, flexibility, and potential for low-cost production, they are emerging as a promising contender for the future of solar energy.

What is perovskite?
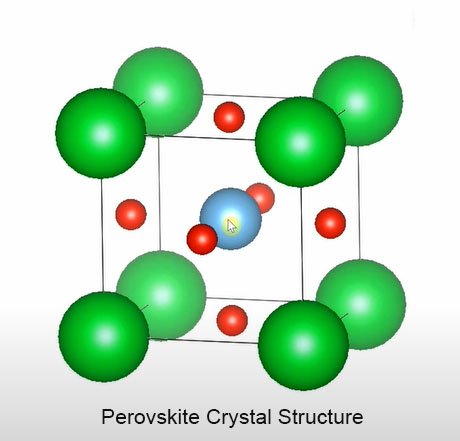
Perovskite refers to a class of materials that share a specific crystal structure, named after the mineral perovskite, which has a similar structure. The general formula for perovskite materials is ABX3, where ‘A’ and ‘B’ are cations, and ‘X’ is an anion. The crystal structure is cubic, with a repeating unit of three different ions.
Perovskite materials have gained significant attention in the field of photovoltaics, specifically in solar cell technology. Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have shown remarkable progress, with the potential for low-cost manufacturing and high efficiency.
What is a perovskite solar cell?
A perovskite solar cell (PSC) is a type of solar cell that uses perovskite-structured materials as the active layer to convert sunlight into electricity.
The active layer in a perovskite solar cell is typically composed of organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite materials. These materials have gained significant attention in recent years because of their exceptional optoelectronic properties, ease of fabrication, and potential for low-cost manufacturing. The structure of perovskite materials allows for efficient light absorption and charge carrier generation.

Benefits of perovskite solar cells
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) offer benefits that make them an exciting area of research and development in the field of photovoltaics. Some of the pros of them are:
- High Efficiency: They have demonstrated the potential to get high power conversion efficiencies. The efficiency levels have rapidly improved and are competitive with traditional silicon solar cells.
- Low-Cost Manufacturing: The fabrication processes for perovskite solar cells are generally simpler. Also, they can be conducted at lower temperatures than traditional silicon solar cells. This simplicity contributes to the potential for cost-effective production.
- Flexibility: Manufacturers could make these types of cells in thin-film form, making them suitable for flexible and lightweight applications. This flexibility allows for integrating solar cells into various surfaces, including curved or irregular shapes.
- Tunability: Researchers could adjust the properties of perovskite materials by changing their chemical composition. This will allow them to optimize the material for specific performance characteristics. This tunability enhances the versatility of them for different applications.
- Rapid Advancements: The field of perovskite solar cells has seen rapid advancements in a relatively short period. Researchers continue to discover new materials and fabrication techniques, improving efficiency, stability, and scalability.
Despite these benefits, they face challenges, particularly related to stability and long-term performance. Issues such as sensitivity to moisture and the need for improved encapsulation technologies are areas of active research.

Why perovskite solar cells are not used?
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are still in research and development. Then, commercial deployment was gradually progressing. Several challenges have hindered the widespread adoption of these types of cells:
- Stability Issues: Perovskite materials are sensitive to moisture and environmental conditions. So, this can degrade their performance over time. Researchers are actively working on improving the stability of them to ensure they can withstand long-term exposure to varying climates.
- Scale-Up Challenges: While they have shown promising results in small-scale laboratory settings, scaling up production to meet commercial demands poses challenges. Achieving consistent performance and reliability in large-scale manufacturing processes is essential for market adoption.
- Toxicity Concerns: Some perovskite materials contain toxic elements like lead, raising environmental and health concerns. Researchers are exploring lead-free alternatives to address these issues and improve the overall sustainability of perovskite solar cells.
- Standardization and Certification: The commercialization of any new technology, including perovskite solar cells, requires adherence to industry standards and certification processes. Developing standardized testing methods and ensuring the safety and reliability of them are ongoing considerations.
- Competition with Established Technologies: Traditional silicon-based solar cells have been widely deployed and have a well-established manufacturing infrastructure. Perovskite solar cells face competition from these mature technologies, and their adoption may require overcoming market inertia.
Despite the cons, there has been significant progress in addressing the limitations of perovskite solar cells. Ongoing research focuses on enhancing stability, developing scalable manufacturing processes, and exploring alternative materials. Some companies and research institutions are actively working on pilot projects and collaborations to bring them closer to commercial viability.
What is the future of perovskite solar cells?
The future of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) holds great promise. So, ongoing research and development suggest several potential directions and advancements:
- Increased Efficiency: Researchers continue to work on optimizing the composition and structure of perovskite materials to enhance their light absorption and charge carrier properties. This could lead to even higher efficiencies, potentially surpassing those of traditional silicon solar cells.
- Improved Stability: Addressing stability concerns is crucial for the commercial viability of PSCs. Scientists are exploring various strategies, such as encapsulation techniques and the development of more stable perovskite formulations. Their goal is to extend the lifespan and reliability of perovskite solar cells.
- Lead-Free Perovskites: Researchers are actively exploring lead-free alternatives to mitigate environmental and health concerns associated with lead in certain perovskite materials. Developing lead-free perovskite formulations could enhance the sustainability and acceptance of PSCs.
- Scalable Manufacturing: Efforts are underway to scale up the production of perovskite solar cells for commercial use. Optimizing manufacturing processes, ensuring consistency in large-scale production, and addressing cost-effectiveness are critical factors for widespread adoption.
- Tandem Solar Cells: Combining them with other materials, such as silicon, in tandem configurations could unlock synergies and improve overall efficiency. Tandem solar cells aim to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, maximizing energy conversion.
- Diversified Applications: The flexibility of PSCs makes them suitable for various applications beyond traditional solar panels. Flexible and lightweight perovskite solar cells could be integrated into building materials, clothing, and other surfaces, expanding their potential use cases.
- Commercial Deployment: As research progresses and stability concerns are addressed, these types of cells are likely to see increased commercial deployment. Pilot projects, collaborations with industry partners, and advancements in manufacturing processes will play a role in bringing PSCs to the market.

Conclusion
The active research community and industry interest suggest a positive outlook for the future of perovskite solar cells. As technologies mature, they could become a significant player in the global solar energy landscape. So, they would offer a combination of high efficiency, flexibility, and potentially lower production costs.




Leave a Reply