What is the difference between an on grid and off grid solar system? The use of solar panels has become an increasingly well-known option for those who want to reduce their carbon footprint, reduce costs on their electricity bills, and avoid power outages and lack of electricity supply. The photovoltaic system is the ideal alternative to convert sunlight into usable electrical energy for homes, businesses and agriculture.

Components of a photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system consists of several components:
1)the solar panels, which capture solar energy;
2)the inverter, which converts the direct current generated by the panels into alternating current that can be used in a home or business;
3)Batteries, which can be optional, and serve to store the energy generated by the solar panels for later use.
There are different types of photovoltaic solar systems. So, it’s important to understand that choosing one or the other will depend on several factors.
Different Types of Photovoltaic Systems
There are different types of photovoltaic solar systems. So, it’s important to understand that choosing one or the other will depend on several factors:
1) geographical location,
2) connection or lack of connection to the electrical grid
3) the use that you will give to the generated energy.
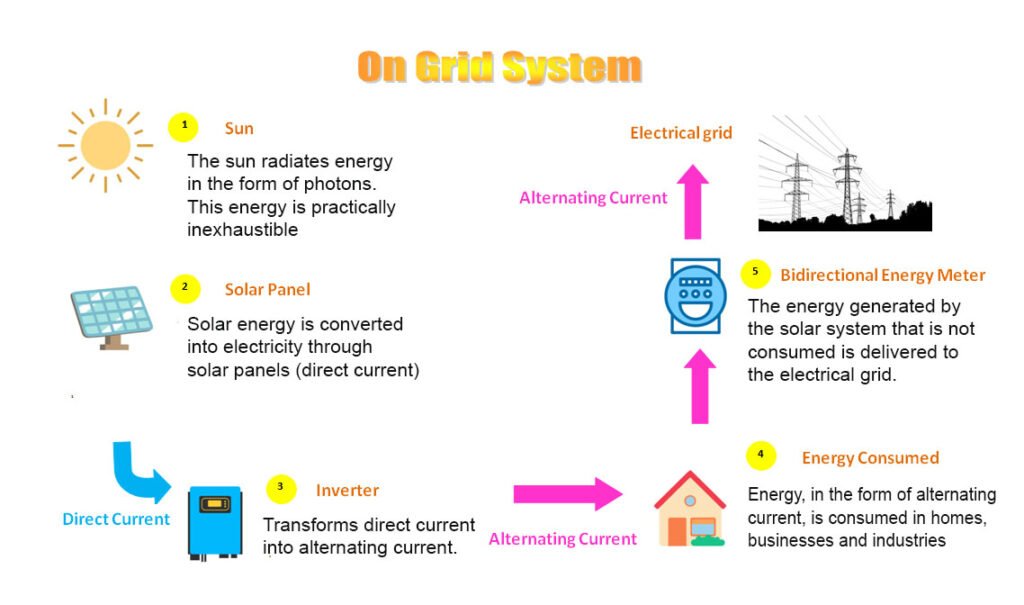
On-Grid System
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is a solar power system that is connected to the local electrical grid. This type of solar system works with the existing utility power grid, allowing the user to draw electricity from both the solar panels and the grid as needed.
Key features of an on-grid solar system include:
- Solar Panels: You can install Photovoltaic (PV) panels on the rooftop or in an open area to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Inverter: The solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which an inverter converts into alternating current (AC). AC is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
- Grid Connection: The inverter is connected to the electrical panel of the building and to the utility grid. The building draws electricity from the solar panels first. And if you need more power than the solar panels can provide, you can supplement it with the grid.
- Net Metering: In many on-grid systems, a net meter is installed. This device measures the amount of electricity generated by the solar panels and the amount consumed by the grid. If the solar system generates more electricity than the building consumes, the excess is fed back into the grid. Conversely, if the building requires more power than the solar panels produce, it can draw from the grid.
- Grid as a Backup: An on-grid solar system doesn’t typically include energy storage (like batteries). Therefore, it relies on the grid as a backup during periods when the sun isn’t shining, such as at night or cloudy days.


Advantages of on-grid solar systems include the potential for cost savings through reduced electricity bills and the ability to earn credits through net metering. However, they do not provide energy independence during grid outages, as they are designed to shut down for safety reasons when the grid goes down (to prevent feeding electricity into the grid and endangering utility workers). For this reason, some users may opt for a hybrid system that includes energy storage for backup power.
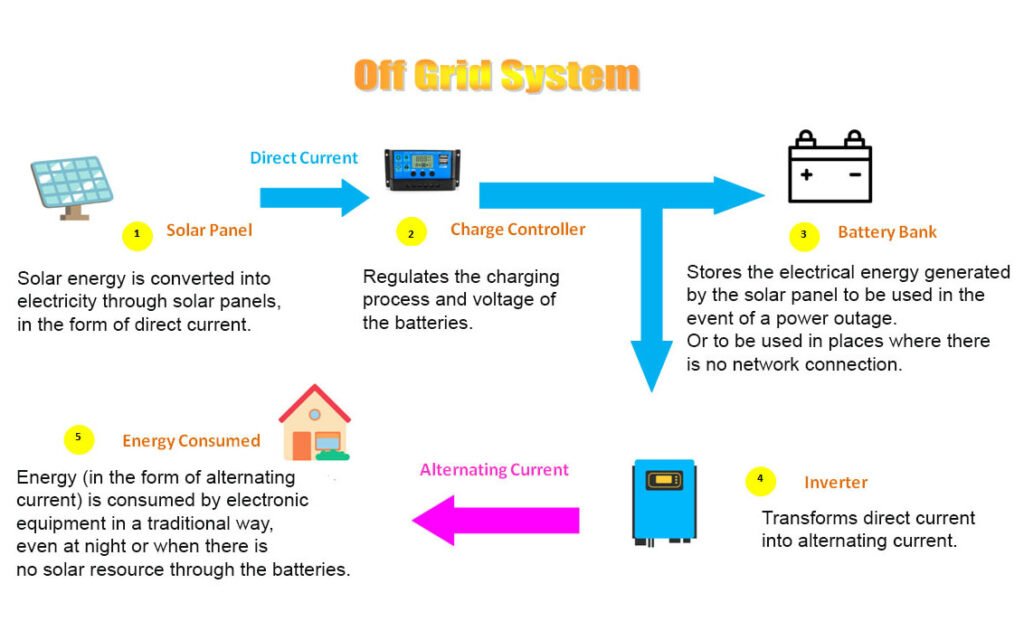
Off- Grid System
An off-grid solar system is a stand-alone, independent power generation system that is not connected to the electrical grid. Unlike on-grid solar systems that rely on the grid for backup or to supply additional power when needed, off-grid solar systems operate autonomously and provide electricity for locations that are not connected to the utility grid. You can use these systems in remote areas, isolated communities, cabins, boats, or for emergency backup power.
Key components of an off-grid solar system include:
- Solar Panels (PV Modules): Off-grid solar systems have solar panels that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. The electricity generated during the day is used to charge batteries for nighttime or cloudy-day use.
- Charge Controller: A charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries. It prevents overcharging of the batteries, which can damage them and ensures efficient charging.
- Battery Bank: Off-grid systems incorporate a battery bank to store excess electricity generated during sunny periods. Batteries store energy for use when the sun is not shining, such as during the night or on cloudy days.
- Inverter: An inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity stored in the batteries into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in most homes and appliances.
- Backup Generator (Optional): Some off-grid systems include a backup generator powered by fossil fuels (e.g., diesel or propane) to provide additional power during extended periods of low sunlight or high demand.
- Energy Monitoring and Control Systems: Off-grid systems may include monitoring and control systems to track energy production and consumption, manage battery charging and discharging cycles, and optimize overall system performance.
Off-grid solar systems offer energy independence to users in areas without access to the electrical grid. They are particularly useful in remote locations where extending grid infrastructure is impractical or cost-prohibitive. However, these systems require careful design and sizing to ensure they can meet the energy needs of the user, especially during periods of low sunlight. Additionally, users may need to manage their energy consumption to align with the available solar power.
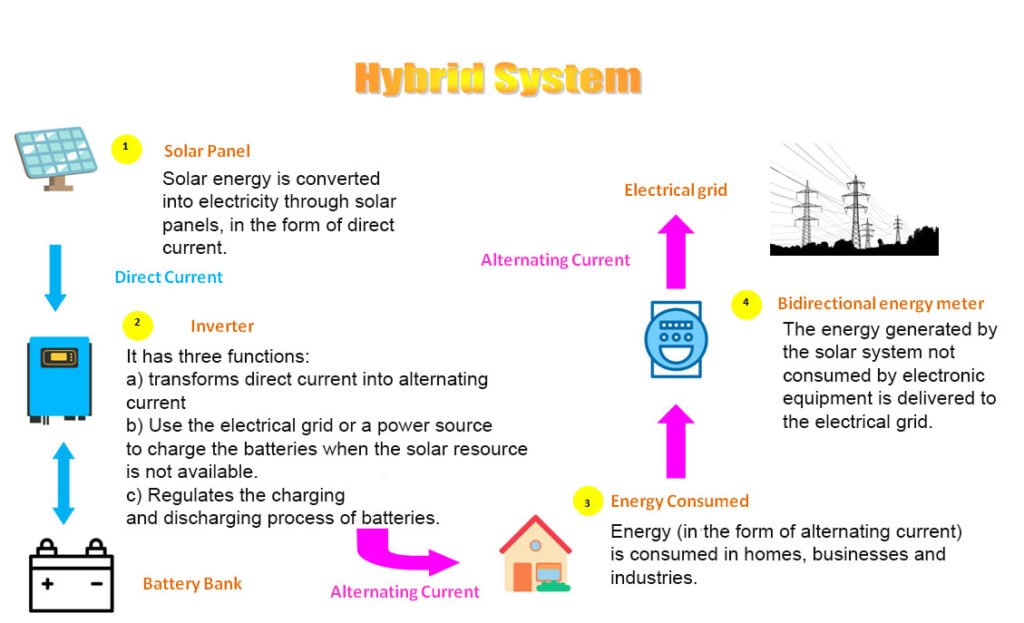
Hybrid Photovoltaic System
A hybrid photovoltaic (PV) system, also known as a solar hybrid system, combines solar power generation with another source of energy, often a conventional power generator or an energy storage system. The goal of a hybrid PV system is to provide a more reliable and continuous power supply. This is useful especially in situations where solar energy alone may be insufficient or inconsistent. These systems are commonly used in both on-grid and off-grid applications.
Key components of a hybrid photovoltaic system include:
- Solar Panels (PV Modules): The solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Charge Controller: In an off-grid or hybrid system, a charge controller is used to regulate the charging of batteries from the solar panels. It helps prevent overcharging and ensures efficient battery charging.
- Battery Storage: Hybrid systems often include energy storage in the form of batteries. The batteries store the excess electricity that the solar panels generate during periods of high sunlight. So, you can use this excess electricity during periods of low sunlight or at night.
- Inverter: The solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity. So, the inverter converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC) for use in household appliances or other electrical devices.
- Backup Power Source (Optional): A hybrid PV system may incorporate a backup power source, such as a diesel generator or another conventional power generator. They use these to provide additional electricity during periods of high demand or extended periods of low sunlight.
- Energy Management System: Hybrid systems often use sophisticated energy management systems to optimize the use of solar power, battery storage, and backup power sources. These systems can prioritize different power sources based on factors such as cost, availability, and system efficiency.
Hybrid photovoltaic systems offer several advantages, including increased reliability, and energy independence. Also, they have the ability to balance power supply and demand more effectively. These systems are commonly used in areas with intermittent grid access. Besides, they are common in residential and commercial settings where a reliable and consistent power supply is crucial.
Advantages and disadvantages of any system
On-Grid Solar System
Pros
Cons
Off Grid Solar System
Pros
Cons
Hybrid Solar System
Pros
Cons
Off Grid and On Grid Solar: Choosing the Right System
- Consider Your Location: If you are in a remote area without grid access, an off-grid or hybrid system may be more suitable. If grid access is available and reliable, an on-grid or hybrid system could be a good fit.
- Energy Needs: Assess your energy consumption patterns. And determine if you need constant power (hybrid/off-grid) or if occasional grid outages are acceptable (on-grid).
- Budget: Consider your budget for both initial installation and long-term maintenance. Off-grid and hybrid systems typically have higher upfront costs.
- Environmental Impact: If reducing your environmental impact is a priority, all three systems contribute to a cleaner energy mix. However, off-grid and hybrid systems with energy storage can maximize renewable energy utilization.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific circumstances and preferences. Consulting with a solar energy professional can help you determine the most suitable solar system for your needs.




Leave a Reply