The photovoltaic industry is always exploring innovative manufacturing processes, whether it be new materials, solar cells, or module designs to maximize performance and reduce the final cost of energy. One of the latest technologies is heterojunction solar cells. These combine classic crystalline silicon and amorphous/thin-film cells, which in theory provide the best of both worlds. So, heterojunction solar cells offer higher efficiency to maximize solar panel performance. In this article, we talk about heterojunction solar cells, how this technology works, and the advantages it offers.

What are Heterojunction Solar Cells?
Heterojunction (HJT) solar cells combine two different technologies in a single cell: a crystalline silicon cell sandwiched between two layers of “thin film” amorphous silicon. Because the junction is formed by two different types of silicon, this technology is known as heterojunction.
This technology was developed by SANYO (now Panasonic) in the 1980s. The first HJT modules had an efficiency of 14.4% and produced 170Wp. Today, panels with HJT cells can reach maximum efficiencies of up to 22% (25% in the laboratory) and powers exceeding 400Wp.
It is currently the most effective process in the solar industry for increasing efficiency and maximizing power output. It even surpasses the performance of PERC solar cells, the current reference technology in the solar industry. And this is because heterojunction technology combines the advantages of thin film absorption and passivation properties of amorphous silicon, with the benefits of crystalline silicon solar cells.
In short, two structurally different semiconductors form the cell. So, HJT technology represents a combination of different semiconductor technologies.
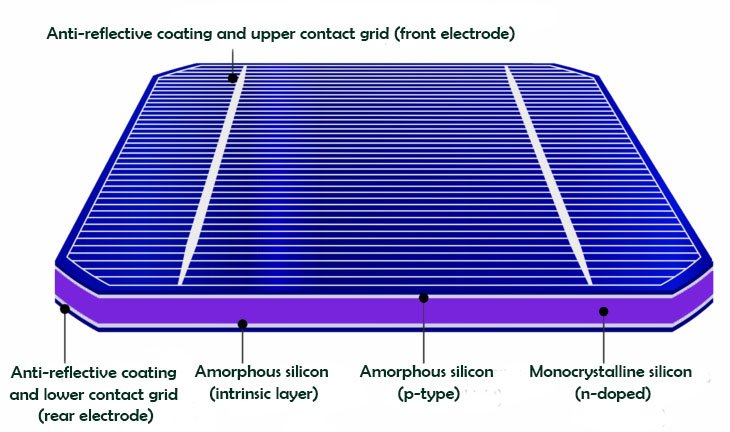
How do solar cells with heterojunction technology work?
As we said, heterojunction solar panels are composed of three layers of photovoltaic material: a layer of crystalline silicon sandwiched between two layers of amorphous silicon “thin film”.
The top layer of amorphous silicon captures sunlight before it reaches the crystalline layer, as well as the light that is reflected by the lower layers. However, monocrystalline silicon, the middle layer, is responsible for converting most of the sunlight into electricity. Finally, behind the crystalline silicon is another layer of thin-film amorphous silicon. This final layer captures the remaining photons that make it past the first two layers, making the most of the sunlight capture.
Thin layers of intrinsic amorphous silicon doped with phosphorus are applied to both sides of n-type solar cells to produce the electrical structures of heterojunction solar cells. Then, transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layers are added to absorb the generated energy. There is also the possibility of doping with boron. This would be the case for p-type solar cells.

Advantages of Heterojunction Solar Cells
The main benefits of heterojunction solar cells are:
- HIGHER EFFICIENCY: Most HJT panels currently on the market have 19.9% to 22% efficiencies. An example would be Canadian Solar’s new HiHero solar panels, which reach a maximum efficiency of 22%. However, efficiencies of 25% and higher are already being reported in the laboratory, which is a great improvement compared to other conventional monocrystalline cells.
- COST SAVINGS: The amorphous silicon used in heterojunction solar cells requires shorter manufacturing times than other technologies. Because of their simplified manufacturing process, heterojunction solar cells have the potential to be cheaper than conventional solutions.
- BETTER HIGH-TEMPERATURE PERFORMANCE: Heterojunction solar cells have a lower temperature coefficient because of the thin film: -0.23%/°C, compared to -0.35%/°C for standard panels. This means they don’t lose as much energy when the panels heat up in the sun, making them ideal for warmer climates.
- LIFE EXPECTANCY: On average, thin-film PV modules have a life expectancy of up to 25 years. Heterojunction technologies, however, can continue to function perfectly for over 30 years.


What is the future of heterojunction technology?
Given the various advantages of heterojunction solar cells, it is likely that more companies will continue to adopt this technology soon. While PERC technology has been a popular choice in the industry for many years, its complex manufacturing process cannot compete with HJT. Also, PERC does not offer the high-temperature performance benefit of HJT.
The market growth for HJT technology is estimated to be much faster than for traditional cell types. The International Technology Roadmap for Photovoltaics (ITRPV) recently predicted that the market share of heterojunction solar cells would grow to 10% by 2025 and 18% by 2031.
Whether HJT technology becomes more than just a niche part of the market will remain to be seen. However, earlier innovations in photovoltaic efficiency, such as split cells and PERC technology, quickly became widespread once major manufacturers adopted them. So it is possible that something similar could happen with heterojunction solar cell panels.

What are the three types of solar cells?
The three main types of solar cells are:
- Monocrystalline silicon solar cells: Known for their high efficiency and durability.
- Polycrystalline silicon solar cells: They are cheaper but generally less efficient than monocrystalline cells.
- Thin-film solar cells: Lightweight and flexible but less efficient than crystalline silicon cells.
Is HJT better than TOPCon?
Both technologies are highly efficient, but HJT generally offers higher efficiency at the cost of more complex manufacturing and higher initial investment. However, recent advances in mass production techniques are making HJT more competitive. In terms of performance under high-temperature conditions, HJT tends to be better.
Other posts you may be interested in
Examples of Solar Panels with HJT Technology
Some notable brands and models utilizing HJT technology include:
- Panasonic HIT Series: Known for their excellent efficiency and reliability, ideal for residential and commercial applications. Visit the Panasonic Website here.
- REC Alpha Series: These panels feature industry-leading efficiency and low-temperature coefficient. Visit the REC group website here.
- Meyer Burger Panels: A new player in the market, Meyer Burger is making waves with cutting-edge HJT panels that promise superior performance. Visit the Meyer Burger website here.







Leave a Reply