Community solar represents a paradigm shift, providing a gateway for individuals, businesses, and communities to participate in the renewable energy revolution. Join us as we explore the world of community solar, its pros and cons, and understand how it’s reshaping the energy landscape.

What is a community solar?
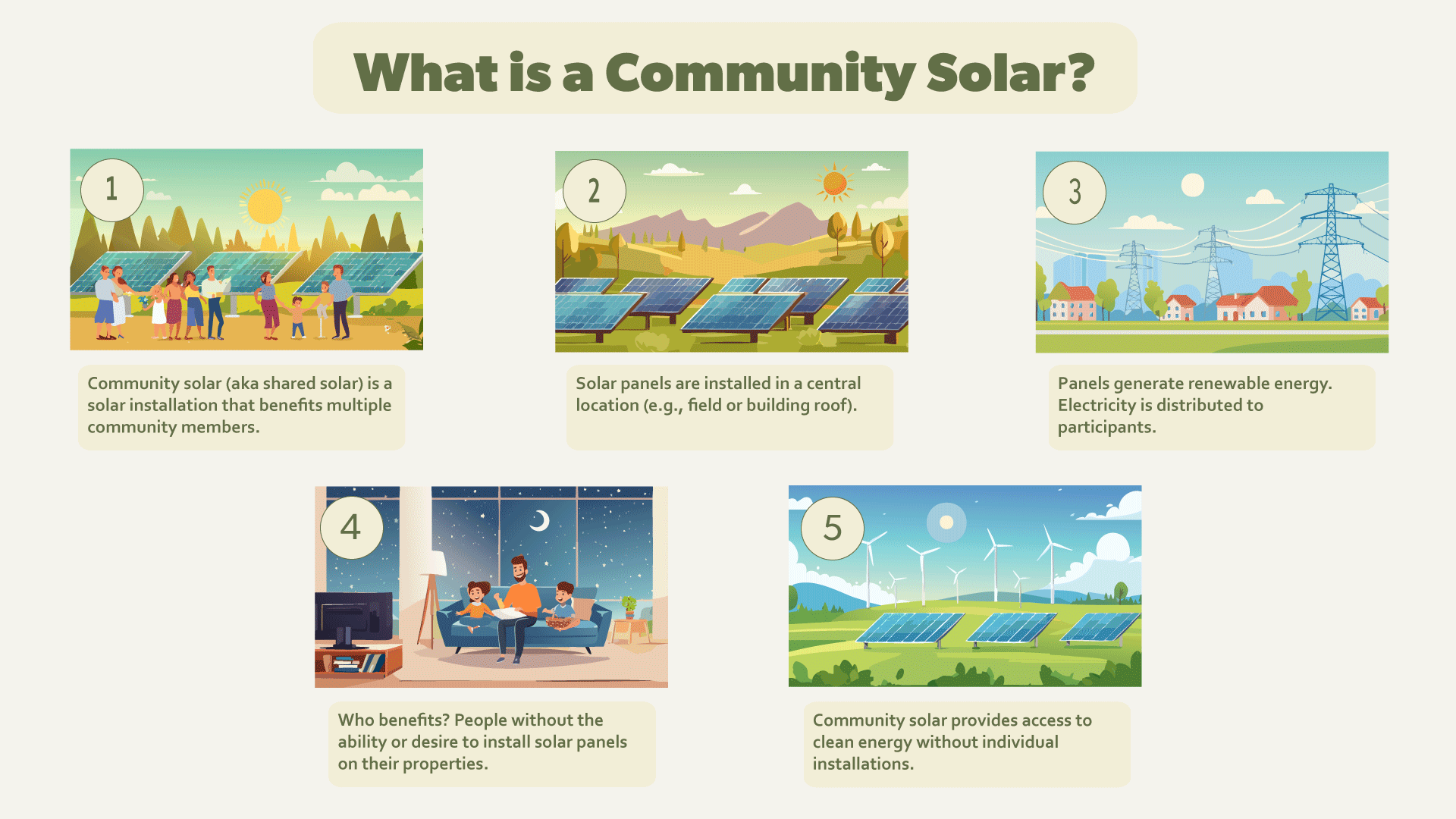
Community solar, also known as shared solar or solar gardens, is a solar power installation that provides benefits to multiple community members. In a community solar project, a solar array typically takes place in a central location, such as a field or on the roof of a building. Next, they generate electricity. Finally, they share it with multiple participants who may not have the ability or desire to install solar panels on their properties.
Here are some key features of community solar:
- Shared Ownership: Participants in a community solar program typically purchase or lease a portion of the capacity of the solar array. This allows them to receive a share of the electricity generated by the system. Besides, they often receive credits on their utility bills based on their share of the output.
- Inclusive Access: They aim to make solar energy accessible to a broader audience. For example, we can include individuals who may not own their homes, have suitable rooftops for solar installations, or have the financial means to invest in a standalone solar system.
- Environmental and Financial Benefits: Participants can benefit from the advantages of solar energy without having to install and maintain their solar panels. Additionally, they may save money on their electricity bills, depending on the terms of the community solar program.
- Local Impact: These projects contribute to local renewable energy generation, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and promoting sustainability. They can also create jobs and stimulate the local economy.
- Regulatory Framework: The success of them often depends on supportive regulatory frameworks. That enables individuals or entities to participate in shared solar programs. Then, they receive appropriate credits or compensation for the electricity they contribute to the grid.
Community solar initiatives vary in structure and design. And they can be implemented by utilities, private companies, or community-based organizations. The primary goal is to make solar energy more accessible, equitable, and sustainable for a broader segment of the population.

How does a community solar work?
The operation of a community solar project involves several key steps. Here’s a general overview of how community solar works:
- Development and Installation: A developer or organization identifies a suitable location for a solar array, such as a field or the roof of a building. Then, it secures the necessary permits and approvals. Finally, they install the solar panels and associated equipment at the chosen location to create a solar array.
- Participant Enrollment: The community solar project is open for enrollment, inviting individuals, businesses, or organizations to participate. Interested participants sign up to purchase or lease a portion of the solar array’s capacity. The size of each participant’s share is typically based on their energy needs and the capacity of the solar installation.
- Credit Allocation: Participants receive credits or a share of the electricity generated by the solar array based on their ownership or subscription level. These credits are often applied directly to participants’ utility bills, reducing their overall electricity costs.
- Utility Connection: The solar array is connected to the local utility grid. This allows the generated electricity to be fed into the grid. The electricity generated by the project offsets participants’ electricity consumption, and credits are applied accordingly.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: The project is monitored to ensure proper functioning and optimal performance. The project conducts maintenance activities, such as cleaning the solar panels and addressing technical issues.
- Billing and Administration: Participants continue to receive regular utility bills, but the bills reflect the credits or savings obtained through their participation in the community solar program.
- Community Engagement: They often involve educational and outreach efforts to engage and inform participants about the benefits of solar energy and the environmental and financial impact of their participation.
It’s important to note that the specific details of how a community solar project operates can vary based on the structure of the program, local regulations, and the goals of the organizing entity. Some projects involve ownership models where participants directly own a portion of the solar installation. On the other hand, other projects may use subscription or lease models. The regulatory environment also plays a crucial role in determining how credits and savings are allocated to participants.
How does a community solar make money?
Community solar projects can generate revenue through various mechanisms. And the financial model often depends on the specific structure of the project. Here are some common ways community solar makes money:
- Participant Payments: Participants in a community solar project typically pay for their share of the solar installation. This can be in the form of upfront payments, ongoing subscription fees, or lease payments. The revenue generated from participant payments helps cover the initial development and installation costs of the solar array.
- Electricity Sales: The electricity generated by the project is usually sold to participants at a rate lower than or competitive with their traditional utility rates. In some cases, they can sell the excess electricity back to the grid, generating additional revenue for the project.
- Subscription or Lease Models: Some projects use subscription or lease models. So, the participants pay a regular fee to receive a certain amount of electricity generated by the solar array. The terms of these agreements may include fixed payments or variable payments based on the amount of electricity produced.
- Renewable Energy Credits (RECs): Community solar projects may generate Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) for the clean energy they produce. So, you can sell these RECs to utilities or other entities looking to meet renewable energy targets. Selling RECs can provide an additional revenue stream for them.
- Tax Incentives and Grants: In some regions, community solar projects may benefit from tax incentives, grants, or subsidies provided by government agencies to encourage the development of renewable energy projects. These financial incentives can help offset initial costs and improve the overall economic viability of the project.
- Long-Term Contracts: These projects may enter into long-term contracts with participants, utilities, or other entities to sell the electricity they generate at predetermined rates. Long-term contracts provide revenue stability and help secure financing for the project.
- Utility Partnerships: Some projects involve partnerships with utilities. Then, the utility agrees to purchase the electricity generated by the solar array or offers billing credits to participants. These partnerships can enhance the financial viability of the project and facilitate grid integration.
It’s important to note that the specific revenue streams and financial model of a community solar project can vary based on many factors. For example, local regulations, project ownership structures, and the goals of the organizing entity. Additionally, ongoing operational, maintenance and financing financing costs play a role in determining the overall financial success of them.
Pros and cons
Community solar projects offer various advantages and disadvantages. And their effectiveness depends on factors such as project design, local regulations, and community engagement. Here are some key pros and cons of them:
Pros
Cons
In evaluating community solar opportunities, it’s crucial to consider the specific characteristics of the project. So, you should think about the local context and the preferences of potential participants. Additionally, addressing regulatory, financial, and technical challenges is essential for the successful implementation of community solar initiatives.

Community solar vs rooftop solar panels
Community solar and rooftop solar panels are two distinct approaches to harnessing solar energy, each with advantages and cons. Here’s a comparison between the two:
Community Solar:
Pros
Cons
Rooftop Solar Panels:
Dos
Don’ts
In summary, the choice between community solar and rooftop solar depends on individual circumstances, preferences, and the specific goals of the energy consumer. Community solar is more inclusive and cost-effective for those without suitable rooftops. On the other hand, rooftop solar offers greater control and energy production for homeowners with the necessary resources and space. Additionally, some individuals may find that a mix of both approaches best meets their energy needs.
How to choose the best community solar
Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to find the community solar project that aligns perfectly with your goals.
1. Assess Your Energy Needs:
Before diving into the world of community solar, evaluate your energy consumption. Understand your average monthly usage and peak demand periods. This knowledge will guide you in selecting a project that can meet your specific energy requirements.
2. Research Local Providers:
Investigate community solar providers in your area. Look for reputable companies with a proven track record in developing and managing solar projects. Online reviews, testimonials, and word-of-mouth recommendations can provide valuable insights into the reliability and credibility of these providers.
3. Understand the Subscription Model:
Community solar often operates on a subscription-based model. Dive into the details of the subscription agreement – understand the terms, duration, and any potential escalations in subscription costs. Clarity on these aspects will prevent surprises and ensure a transparent commitment.
4. Evaluate Project Credibility:
Scrutinize the specifics of the project. Assess the track record of the developer – have they completed similar projects in the past? Reliable developers ensure the longevity and efficiency of the solar farm, safeguarding your investment.
5. Compare Financial Benefits:
One of the primary attractions of community solar is its potential for cost savings. Compare the financial benefits offered by different projects. Analyze subscription rates, potential savings on your electricity bill and any additional perks. For example, fixed-rate guarantees or renewable energy credits.
6. Review the Project’s Location:
The geographical location greatly influences the efficiency of a solar farm. A project in an area with ample sunlight will yield better results. Investigate the solar potential of the location and ensure that it aligns with your expectations for energy generation.
7. Inquire About Transferability:
Life is dynamic, and circumstances may change. Inquire about the transferability of your subscription in case you move or need to make adjustments. Flexibility ensures you can seamlessly continue benefiting from community solar even if your living situation evolves.
8. Check for Regulatory Compliance:
Ensure that the community solar project complies with local regulations and standards. Projects adhering to industry best practices and regulatory guidelines are more likely to be reliable and sustainable over the long term.
9. Seek Community Engagement:
A strong sense of community is often a hallmark of successful community solar projects. Inquire about opportunities for community engagement, whether through regular updates, events, or educational initiatives. Being part of an engaged community can enhance your overall experience.
10. Consult with Experts:
If navigating the complexities of community solar feels overwhelming, consider seeking advice from renewable energy experts or consulting services. Professionals in the field can provide tailored guidance based on your specific needs and help you make an informed decision.
Choosing the best community solar project involves research, careful consideration, and understanding your unique energy requirements. By following these steps, you can embark on your journey towards sustainable, community-driven energy with confidence and clarity.
Is a Community Solar Available Near You?
Community solar projects in the UK are often initiated at the local level. They involve community groups, local authorities, or renewable energy cooperatives. Here is a list of some of the most popular solar communities in the UK:
- Reach Community Solar Farm: They’ve built a community solar farm near Reach. The solar farm is owned and run by a cooperative of local people. So, they generate enough clean, green electricity to power 50 houses – about half the village.
- WWCE: Wiltshire Wildlife Community Energy (WWCE) develops community-owned renewable energy projects that reduce carbon emissions and create more wildlife in Wiltshire.
- Big Solar Co-op: The Big Solar Co-op is a not-for-profit, carbon-first and volunteer-led organisation. They’re solarising commercial and community buildings all over the UK from doctors’ surgeries to factories and everything in between.
- Bristol Energy Cooperative: Bristol Energy Cooperative develops renewable energy and energy efficiency projects, with and for the benefit of the community.
- NLCE: North Lincolnshire Community Energy (NLCE) has been established to break down the barriers and accelerate the uptake of renewable energy in the region. They aim to drive the area forward in our challenge to be a net zero carbon emitting area by 2030.
- Westmill Solar: The project aims to combat climate change by financing a reliable source of renewable energy. As a result, they provide local people and other investors with a stable, reliable source of income. Also, they help the area transition to a low-carbon future economy. The project generates 4.8 GWh per year of clean electricity, enough to power 1,400 homes.
- M&S Energy Society: Launched in 2016, M&S Energy Society was the first retail-led community energy society. The initiative aimed to generate renewable electricity from solar panels installed on M&S stores across the UK. The share offer gave M&S customers and the public the special opportunity to invest in the project. So, the income from the electricity generated by the panels provides a return for investors and funding carbon-saving initiatives in the local community.
- Edinburgh Community Solar Co-operative: Edinburgh Community Solar Co-operative owns and operates 30 solar panel installations throughout Edinburgh. They have a total generating capacity of 1.38MW. You can find these panels in Edinburgh Council schools, community centres and leisure facilities. Each year we generate approximately 1.1GWh of clean, renewable electricity for these buildings and the wider grid. After providing a fixed return on their members’ investments, they invest the excess profits in community projects throughout Edinburgh that promote sustainability and renewable energy.
For more information, visit also the following websites:
Conclusion
In short, community solar is an innovative and inclusive approach to harnessing the power of the sun for clean energy. As the world shifts towards more sustainable practices, community solar stands out as a promising solution for individuals and communities looking to make a positive impact on the environment and their energy bills.




Leave a Reply