Solar arrays are one of the key components of the solar power system. This article explains the concept of solar arrays, exploring their types, sizes, and installation processes.

What is a solar array?
A solar array is a collection of solar panels (also known as solar modules or photovoltaic modules) arranged in a specific configuration to generate electricity from sunlight. Solar panels convert sunlight into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect, where certain materials generate an electric current when exposed to light.
The solar array typically consists of multiple solar panels connected to form a larger unit. These arrays can vary in size, from small rooftop installations on homes to large-scale solar farms covering extensive land areas. The arrangement and orientation of the solar panels in an array are optimized to capture as much sunlight as possible and convert it into electricity efficiently.
What is the difference between a solar cell panel and a solar array?
We often use the terms “solar panel” and “solar array” interchangeably. But it’s essential to understand the distinction between them. A solar panel refers to a single unit that contains multiple solar cells, which are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. On the other hand, a solar array comprises multiple solar panels interconnected to form a larger system.
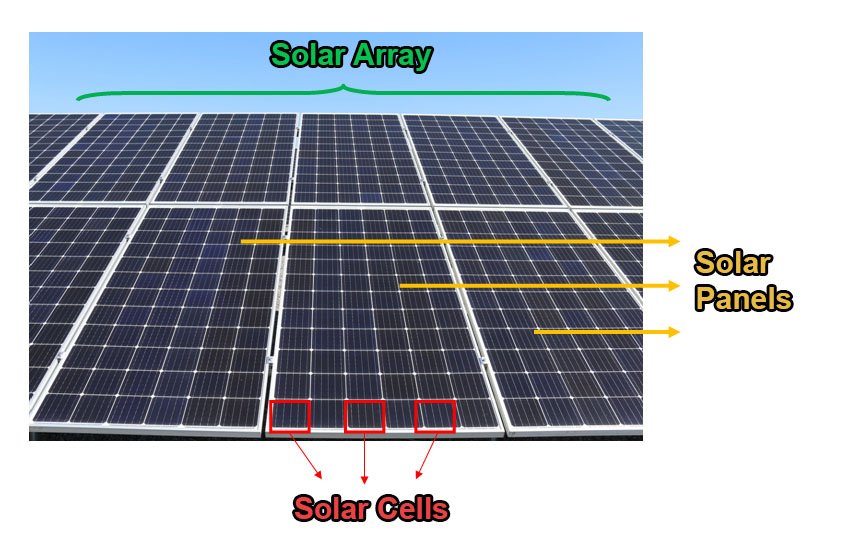
What is the difference between a solar panel and a solar array?
A solar panel and a solar array are related concepts, but they refer to different components in the context of solar energy systems.
Solar Panel:
A solar panel, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) module, is a single unit that generates electrical power from sunlight. It consists of multiple solar cells made of semiconductor materials (such as silicon) that convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Solar Array:
A solar array is a collection of multiple solar panels arranged in a specific configuration to generate electricity. It is essentially a grouping or combination of individual solar panels working together.
Number of Panels in an Array
The number of solar panels in a solar array can vary widely depending on several factors, including the following:
- Power Requirements: The total power output needed determines the number of panels required. Larger power requirements may necessitate a greater number of panels.
- Panel Capacity: The wattage or capacity of individual solar panels also plays a role. Higher-capacity panels can generate more electricity. That means you may need fewer panels to meet a specific power requirement.
- Location and Sunlight Conditions: The amount of sunlight a location receives affects the efficiency of solar panels. As a result, you might need fewer panels in areas with abundant sunlight than in less sunny regions.
- System Efficiency: The overall efficiency of the solar power system, including factors such as inverter efficiency and system losses, can impact the number of panels needed.
- Space Available: The available space for installing solar panels influences the layout and arrangement of the array. In limited spaces, we recommend choosing higher-capacity panels.
- Financial Considerations: Budget constraints and financial considerations may influence the decision on the number of panels you should install. Balancing cost and performance is a key consideration.
- Government Incentives and Regulations: Incentives, rebates, and regulations related to solar energy in a particular region can also impact the decision on the size of the solar array.
How big is a 1 MW solar array?
The size of a 1 megawatt (MW) solar array can vary depending on the efficiency of the solar panels used. On average, a 1 MW solar array may cover an area of approximately 5 acres, with around 2,500 to 3,000 solar panels.
What is the best type of solar array?
The “best” type of solar array depends on various factors, including the specific needs, goals, and constraints of a given project. In other words, you can find different types of solar arrays for different applications and conditions.Here are some common types of solar arrays:
Roof-Mounted Solar Arrays:
- On-grid Rooftop Solar: These are solar arrays that you can mount on the rooftops of residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. Besides, you can connect them to the local power grid and can offset electricity consumption.
- Off-grid Rooftop Solar: Suitable for locations without access to the grid, these systems use batteries to store excess energy for use when the sun is not shining.
Ground-Mounted Solar Arrays:
- Solar Farms: Solar Farms are large-scale installations with solar panels mounted on the ground. So, they are designed to generate significant amounts of electricity and are often used for utility-scale power production.
Floating Solar Arrays:
Also, you can install solar panels on bodies of water, such as lakes, ponds, or reservoirs. Floating solar arrays can be an effective use of space and can help reduce water evaporation.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV):
Integration of solar panels into building materials, such as solar roof tiles, solar windows, or solar facades. BIPV can blend with the architecture and serve dual purposes of generating electricity and acting as building elements.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Arrays:
Use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, typically a receiver. This concentrated heat is then used to generate steam, which drives a turbine to produce electricity.
Solar Tracking Systems:
Mechanisms that allow solar panels to follow the movement of the sun throughout the day, optimizing the angle of sunlight incidence for increased energy production.
Portable Solar Arrays:
Compact and mobile solar panels are perfect for applications such as camping, hiking, or emergency power. So, you can fold or roll them up for easy transport.

How to install your own solar array
While installing your solar array can be a rewarding DIY project, it’s important to note that working with electricity and installing solar panels involves certain risks. We recommend consulting with a professional or hiring a licensed solar installer if you’re not experienced with electrical systems to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations. Here’s a general guide on how to install a solar array:
- Evaluate Your Energy Needs: Determine your energy consumption to size the solar array appropriately. Consider factors like your average daily electricity usage, peak demand, and any future changes in energy needs.
- Conduct a Site Assessment: Evaluate your property for sunlight exposure, shading, and available space. Ensure that the roof or ground area selected for installation receives ample sunlight throughout the day.
- Design Your Solar Array: Choose the type of solar panels, inverters, and mounting system based on your needs and site conditions. You may use online solar design tools or consult a professional to create an efficient system.
- Obtain Necessary Permits: Check with your local authorities to determine the required permits for solar installations. Obtain all necessary approvals before starting the installation.
- Gather Materials and Equipment: Purchase the solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, wiring, and other necessary equipment. Ensure that all components meet safety and performance standards.
- Install Mounting System: Install the mounting structure on the roof or the ground. Ensure that you attach it securely and it follows the design specifications. Roof installations may involve penetrating the roof, so waterproofing is crucial.
- Install Solar Panels: Attach the solar panels to the mounting structure according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Connect the panels in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current.
- Install Inverters: Install inverters to convert the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) for your home. Besides, we recommend mounting them near the main electrical panel.
- Connect Wiring: Connect the wiring from the solar panels to the inverters and from the inverters to your home’s electrical panel. Follow electrical codes and guidelines to ensure safe and compliant installations.
- Testing and Commissioning: Test the system to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Check for any electrical issues and verify that the solar array is generating electricity as expected.
- Final Inspection: Contact your local building department for a final inspection to ensure the installation meets all safety and code requirements.
Can you install more than one solar array?
Yes, it is possible to install more than one solar array, especially for larger properties or commercial installations. So, you can interconnect multiple arrays to create a more extensive and efficient solar power system. Proper planning and design are essential to maximize energy production and system performance.
Other posts you may be interested in
Conclusion
Whether you are considering a residential rooftop installation or a large-scale solar farm, grasping the fundamentals of solar arrays empowers individuals and businesses to harness the sun’s power for a cleaner and greener tomorrow.






Leave a Reply