What is a bifacial solar panel? This is a technology that is revolutionizing the way we capture and convert sunlight into clean, renewable energy. Keep on reading if you want to know more.
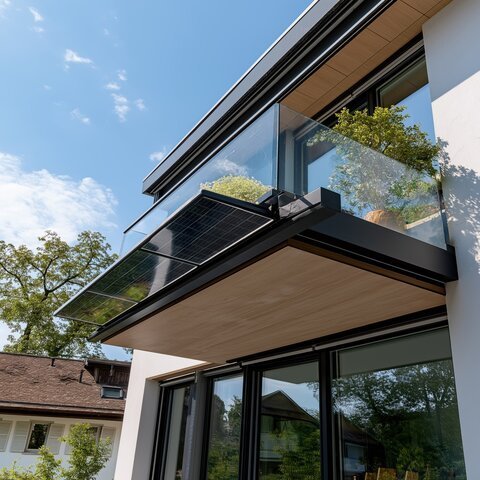

What is a bifacial solar panel?
A bifacial solar panel is a type of solar module designed to capture sunlight from both the front and rear sides, hence the term “bifacial” (meaning two-faced). Unlike traditional solar panels that only have photovoltaic cells on one side, bifacial panels have cells on both the front and back surfaces. This design allows them to capture reflected sunlight from the ground or nearby surfaces, increasing their overall energy yield.
How do bifacial solar panels work?
Bifacial solar panels work by capturing sunlight on both the front and rear surfaces of the solar cells. This dual-sided design allows them to harness not only direct sunlight from above but also reflected sunlight from surrounding surfaces, known as the albedo effect. Here’s how bifacial solar panels work:
- Front-Side Absorption: Like traditional monofacial solar panels, bifacial panels have photovoltaic cells on their front side. So, when exposed to sunlight, these cells absorb photons, generating an electric current through the photovoltaic effect.
- Reflected Light (Albedo Effect): Bifacial panels are positioned to capture sunlight that is reflected off nearby surfaces, such as the ground, vegetation, or buildings. This reflected light contributes additional energy to the solar cells on the front side.
- Rear-Side Absorption: The rear side of the bifacial panels also has a layer of photovoltaic cells. This allows them to capture sunlight that passes through the panel or is reflected onto the rear surface. Besides, the rear-side cells generate additional electricity.
- Transparent Backsheet or Glass: Bifacial solar panels typically use a transparent back sheet or glass on the rear side to allow sunlight to reach the rear cells. So, this design maximizes the exposure of the rear cells to the reflected light.
- Mounting Configuration: Bifacial panels are installed with a mounting configuration that allows light to reach both sides. This may involve elevated mounting structures, such as tracker systems that follow the sun’s path, or installing panels on surfaces that reflect light effectively.
- Optimization with Tracking Systems: Bifacial panels can be further optimized when used in conjunction with solar tracking systems. In other words, solar trackers adjust the orientation of the panels throughout the day to follow the sun’s movement, maximizing the exposure of both sides to direct sunlight and reflected light.
- Increased Energy Yield: The ability to capture both direct and reflected sunlight allows bifacial solar panels to achieve a higher energy yield than traditional mono-facial panels, especially in environments with high reflectivities, such as snowy landscapes, sandy surfaces, or areas with light-coloured ground cover.
- Site-Specific Considerations: The effectiveness of bifacial solar panels depends on site-specific factors, including the ground cover, inclination angle, and surrounding environment. Different configurations may be optimal for various locations and applications.
Bifacial solar panels are becoming increasingly popular in the solar energy industry due to their potential for higher efficiency and energy production. As technology advances, improvements in design and manufacturing continue to enhance the performance of bifacial panels in various environments.

How much more energy can bifacial solar panels generate?
The additional energy generation from bifacial solar panels compared to traditional monofacial panels depends on various factors, including the specific conditions at the installation site. Also, the amount of additional energy can vary based on the reflectivity of the surroundings, the tilt angle of the panels, and other site-specific considerations. Here are some general considerations:
- Albedo (Reflectivity) of Surroundings: Bifacial panels benefit most in areas with high albedo, which refers to the reflectivity of the surfaces around the solar panels. Surfaces like snow, sand, water, or light-coloured ground cover can enhance the reflection of sunlight onto the rear side of the panels, increasing overall energy capture.
- Panel Tilt and Height Above Ground: The tilt and height of the solar panels above the ground play a role in determining the amount of light that reaches the rear side. Bifacial panels mounted at an optimal tilt and height can capture more sunlight from both sides, contributing to higher energy production.
- Climate and Atmospheric Conditions: Weather conditions, such as cloud cover and atmospheric clarity, can impact the amount of sunlight reaching the rear side of bifacial panels. In consistently sunny and clear environments, these panels are more likely to realize their full potential.
- Technology and Design: Advances in bifacial panel technology and design contribute to increased energy capture. Ongoing research and development aim to enhance the efficiency of these panels, improving their performance under various conditions.
- Tracking Systems: Bifacial panels can benefit significantly from solar tracking systems that follow the sun’s path throughout the day. So, tracking systems help maximize the exposure of both sides of the panels to sunlight, further boosting energy production.
While it’s difficult to provide an exact percentage increase in energy generation, studies and simulations have suggested that bifacial solar panels can achieve additional energy gains in the range of 5% to 30% compared to monofacial panels, depending on the factors mentioned above.
Which is better Bifacial vs Monofacial?
The choice between bifacial and monofacial solar panels depends on various factors, including the specific characteristics of the installation site, the intended application, and budget considerations. Here are some key considerations for both bifacial and monofacial solar panels:
Bifacial Solar Panels:
Pros
Cons
Advantages Explained
- Increased Energy Yield: Bifacial panels can capture sunlight from both the front and rear sides, leveraging the albedo effect. This can result in higher energy production, especially in environments with high reflectivities, such as snowy landscapes or areas with light-coloured ground cover.
- Potential for Higher Efficiency: Bifacial panels have the potential to achieve higher efficiency and energy yields compared to traditional monofacial panels, particularly in specific environments.
- Mounting: We recommend mounting them on elevated structures or tracking systems, allowing for better exposure to sunlight and reflected light.
Disadvantages explained
- Higher Initial Cost: Bifacial panels typically have a higher upfront cost compared to monofacial panels. The increased efficiency and energy production may justify the additional investment, but the economic feasibility depends on the specific conditions of the installation site.
- Site-Specific Performance: The effectiveness of bifacial panels depends on site-specific factors, including ground cover, tilt angle, and surroundings. A thorough site assessment is crucial for optimizing performance.
Monofacial Solar Panels:
Pros
Cons
Advantages Explained
- Lower Initial Cost: Monofacial panels generally have a lower upfront cost compared to bifacial panels. This can be a significant factor for budget-conscious projects.
- Widespread Adoption: Monofacial panels are widely adopted and have a well-established track record. They are a reliable and proven technology with extensive market availability.
- Mounting Flexibility: Monofacial panels offer more flexibility in mounting configurations, as they do not necessarily require elevated structures or tracking systems.
Disadvantages Explained
- Lower Energy Yield in Certain Environments: Monofacial panels do not capture reflected light from the rear side, potentially resulting in lower energy yields in certain environments with limited reflectivity.
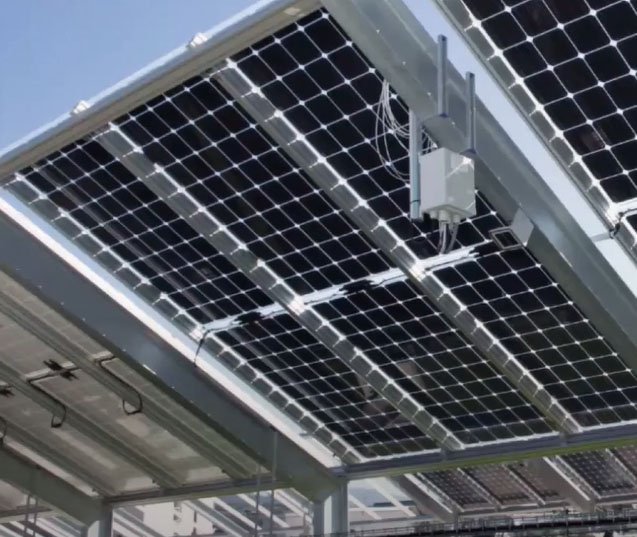

Choosing Between Bifacial and Monofacial:
- Site-Specific Analysis: Conduct a site-specific analysis to assess the ground cover, tilt angle, and environmental conditions. Bifacial panels are generally more effective in locations with high reflectivity.
- Budget and Cost Considerations: Consider the budget constraints of the project. While bifacial panels may offer higher efficiency, the economic viability should be evaluated based on the specific project requirements.
- Installation Type: Evaluate the installation type. Bifacial panels are often more suitable for utility-scale projects or installations where elevated structures or tracking systems can be implemented.
- Technology Advances: Keep abreast of technological advancements. Bifacial panel technology is evolving, and improvements may impact their performance and cost-effectiveness over time.
Finally, the choice between bifacial and monofacial panels depends on the specific goals and conditions of each solar project. Consulting with solar professionals and conducting a thorough site assessment can help determine the most suitable option for a given application.
Pros and cons of bifacial solar panels
Pros
Cons
Pros of Bifacial Solar Panels Explained
- Increased Energy Yield: Bifacial panels can capture sunlight from both the front and rear sides, leveraging the albedo effect. This can result in higher energy production, especially in environments with high reflectivities, such as snowy landscapes or areas with light-coloured ground cover.
- Flexibility in Mounting: People often mount them on elevated structures or tracking systems, allowing for better exposure to sunlight and reflected light. This flexibility in mounting configurations can optimize the energy capture of the panels
- Potential for Higher Efficiency: Bifacial panels have the potential to achieve higher efficiency and energy yields compared to traditional monofacial panels. This is especially advantageous in situations where maximizing energy production is a primary goal.
- Diverse Applications: Bifacial panels can be suitable for various applications, including utility-scale solar power plants, commercial installations, and certain residential setups. So, they are particularly effective in open areas with minimal shading.
- Reduced Temperature Impact: The rear side of bifacial panels is exposed to ambient air, which can help dissipate heat more effectively. This can lead to a reduction in temperature-related efficiency losses compared to monofacial panels.
Cons of Bifacial Solar Panels Explained
- Higher Initial Cost: Bifacial panels typically have a higher upfront cost than monofacial panels. The increased complexity of the design and the additional materials required contribute to the higher initial investment.
- Site-Specific Performance: The effectiveness of bifacial panels is highly dependent on site-specific factors, including ground cover, tilt angle, and surroundings. A thorough site assessment is crucial for optimizing performance, and the benefits may be less pronounced in certain environments.
- Mounting and Installation Complexity: Bifacial panels may require more complex mounting configurations, such as elevated structures or tracking systems. This complexity can increase installation costs and may necessitate specialized expertise.
- Economic Viability: The economic viability of bifacial panels depends on the specific conditions of the installation site and the project budget. You need to weigh the higher efficiency and energy yield against the additional upfront costs.
- Market Availability and Experience: Bifacial panel technology, while advancing, may have a more limited market availability compared to traditional monofacial panels. Some installers and developers may have more experience with monofacial technology.
In summary, the decision to use bifacial solar panels involves a careful evaluation of the specific requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions of each solar project. While bifacial panels offer increased energy potential, you should carefully weigh their higher upfront cost and site-specific considerations against the potential benefits. Advances in technology and increased market adoption may continue to impact the cost-effectiveness and performance of bifacial solar panels over time.
Do bifacial solar panels work on the roof?
You can use bifacial solar panels on roofs, but their effectiveness depends on several factors, and their performance may differ from installations on the ground. Here are some considerations regarding the use of bifacial solar panels on roofs:
- Roof Configuration: The configuration of the roof plays a crucial role in the performance of bifacial panels. For optimal results, the roof should have a reflective surface, such as a white or light-coloured roofing material, to enhance the albedo effect.
- Surrounding Environment: The effectiveness of bifacial panels on roofs is influenced by the surrounding environment. If the roof is in an area with high reflectivity, such as in snowy climates or with nearby light-coloured surfaces, the albedo effect can contribute to increased energy production.
- Tilt Angle and Orientation: The tilt angle and orientation of bifacial panels on a roof impact their exposure to sunlight and reflected light. Roof configurations that allow for an optimal tilt angle or tracking systems can enhance the performance of bifacial panels.
- Shading: Shading from nearby structures, trees, or other obstructions can affect the performance of bifacial panels on a roof. You should conduct a proper shading analysis to minimize the impact on energy production.
- Mounting Systems: Bifacial panels on roofs may require specific mounting systems to ensure proper exposure to both direct and reflected sunlight. So, you can use adjustable or tracking mounting systems to optimize the panel orientation.
- Roof Material and Temperature: The material of the roof and the temperature can impact the efficiency of bifacial panels. Some roof materials may absorb and retain heat, affecting the temperature-related efficiency of the panels. Adequate ventilation and spacing may be necessary.
- Roof Load Capacity: You should consider the weight and additional wind loading of bifacial panels to ensure that the roof structure can support the added load. Also, you often will need engineering assessments to confirm the structural integrity of the roof.
- Installation Costs: The installation of bifacial panels on a roof may involve additional costs related to mounting systems, ventilation, and specific installation requirements. You should evaluate carefully the economic feasibility of bifacial panels on a roof.
While we often associate bifacial panels with ground-mounted installations, there are successful applications on roofs, particularly in specific environments with favourable conditions. Site-specific assessments, shading analyses, and engineering considerations are crucial when planning the installation of bifacial solar panels on roofs.

Bifacial solar panel manufacturers
Here are the most popular bifacial solar panels manufacturers in the UK:
Trina Solar:
Trina Solar is a global leader in the solar industry and offers a range of solar panels, including bifacial modules. They are notorious for their high-efficiency products and have a significant market presence.
JinkoSolar:
JinkoSolar is a major solar module manufacturer that produces both monofacial and bifacial solar panels. They are famous for their commitment to technology and innovation in the solar industry.
LONGi Solar:
LONGi Solar is a Chinese solar company that specializes in mono-crystalline solar products. They produce bifacial solar panels known for their high efficiency and performance.
Canadian Solar:
Canadian Solar is a global solar energy company that manufactures a variety of solar panels. They offer bifacial modules designed to maximize energy capture through both sides of the panel
SunPower:
SunPower is famous for its high-efficiency solar panels, and they also offer bifacial solar panels. We recommend using SunPower’s panels in residential and commercial installations.
LG Solar:
LG Solar, a division of LG Electronics, is popular for its high-quality solar panels. They produce bifacial modules designed for various applications, including residential and commercial installations.
Are bifacial solar panels worth i
Whether bifacial solar panels are worth it depends on various factors, including the specific characteristics of the installation site, project goals, and budget considerations. Here are key factors to consider when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of bifacial solar panels:
1. Installation Site Characteristics:
Reflectivity: Bifacial panels benefit from high reflectivity in the surroundings, such as snow, sand, or light-coloured surfaces. In environments with low reflectivity, the additional gains from the rear side may be limited.
Ground Cover: Ground cover and conditions affecting albedo play a significant role. Bifacial panels may be more effective in open areas with minimal shading.
2. Project Goals:
Energy Yield: If maximizing energy production is a primary goal, especially in environments with favourable conditions, bifacial panels can offer increased energy yield compared to monofacial panels.
Site-Specific Optimization: Bifacial panels may be more suitable for utility-scale projects or larger installations where you can implement optimized mounting configurations and tracking systems.
Higher Initial Cost: Bifacial panels typically have a higher upfront cost compared to monofacial panels. So, consider the budget constraints of the project and evaluate whether the increased efficiency justifies the additional investment.
Cost of Mounting Systems: You may need elevated mounting structures or tracking systems for optimal bifacial panel performance, and these can contribute to overall installation costs.
4. Roof or Ground-Mounted:
Mounting Configuration: We can often associate bifacial panels with ground-mounted installations, where the panels can capture reflected light from the ground. However, you can also use them on roofs with specific configurations and reflective surfaces.
5. Technology and Manufacturer:
Technology Advances: Advancements in bifacial panel technology may impact performance and cost-effectiveness over time. Keep abreast of technological developments in the solar industry.
Manufacturer Reputation: Choose reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality bifacial panels. Besides, consider product warranties and track records.
6. Long-Term Considerations:
Lifespan: Evaluate the expected lifespan of bifacial panels and whether the additional upfront investment aligns with long-term energy production goals.
Technology Evolution: Consider the potential for technology evolution. Bifacial panel technology may see improvements and cost reductions over time.
7. Site Assessment and Analysis:
Professional Consultation: Consult with solar professionals or installers to conduct a site-specific analysis. Shading studies, albedo analysis, and engineering assessments can provide insights into the potential benefits of bifacial panels for a specific location. To sum up, bifacial solar panels can be worth it in certain situations, especially when deployed in environments with high reflectivity




Leave a Reply